The valence electrons which are present in the outermost shell of the atom get distributed in the space lattice of the metal. Such a solid consists of closely packed atoms.
Simple What Metallic Bond With Creative Design, Metallic bond is a type of chemical bond that is formed by the electrostatic attraction of conduction electrons and positively charged metal ions. Metallic bonding is the attraction between the positive ions in a regular lattice and the delocalised electrons.
 Metallic bonding From slideshare.net
Metallic bonding From slideshare.net
All the characteristics metallic properties can be explained on the basis of electron sea model as given below: A metallic bond is a chemical bond, in which the atoms do not share or exchange electrons to bond together. Metallic bonds are formed only between metal atoms. * metallic bonding is the strong electrostatic force of attraction between metal cations/atoms and delocalised electrons in the metallic lattice of a metallic substance (e.g.
Metallic bonding Sap‑3 (eu), sap‑3.a (lo), sap‑3.a.5 (ek) transcript.
Ductility is property of metals for what one can apply stress onto a metal to make it longer or wider without breaking. They can also vary according to. The brain is designed in such a way that it is cleared of. The nature of metallic bonding accounts for many of the physical properties of metals, such as conductivity and malleability.
 Source: thescienceteacher.co.uk
Source: thescienceteacher.co.uk
This is a metallic bond example. In a sample of metal, the valence electrons detach from the. Hence, it is not possible for the metal atoms to form 8 or 12. Metals form giant structures in which electrons. Metallic bonding teaching resources the science teacher.
 Source: sciencenotes.org
Source: sciencenotes.org
Metallic bonds are formed only between metal atoms. The force which binds together the atoms of metals is called metallic bond. Sap‑3 (eu), sap‑3.a (lo), sap‑3.a.5 (ek) transcript. A metallic bond is characterized by the conduction of electricity and heat, which is a result of the free movement of electrons through the matrix of positive metal ions. Metallic Bonding Definition and Properties.
 Source: expii.com
Source: expii.com
In the outer shells of the metal atoms are free to move. Be accompanied by one or more bridging ligands, or unsupported. They can also vary according to. This page introduces the bonding in metals. Metallic Bond — Formation & Compounds Expii.
 Source: obfuscata.com
Source: obfuscata.com
The brain is designed in such a way that it is cleared of. Metallic bond, force that holds atoms together in a metallic substance. What are metallic bonds | properties of matter | chemistry | fuseschoollearn the basics about particles in a metal, which are held together by metallic bonds. During brazing, molten filler metal must wet and flow across the surface of a solid base core alloy of the brazing sheet in order to form a good braze joint or brazing fillet. Strength of Metallic Bonds.
 Source: embibe.com
Source: embibe.com
- metallic bonding is the strong electrostatic force of attraction between metal cations/atoms and delocalised electrons in the metallic lattice of a metallic substance (e.g. This is a metallic bond example. Metals tend to have high melting points and boiling points suggesting strong bonds between the atoms. Ductility is property of metals for what one can apply stress onto a metal to make it longer or wider without breaking. Metallic Bonding Definition, Properties, Examples, Diagram.

Hence, it is not possible for the metal atoms to form 8 or 12. As a consequence, the valence electrons continually move from one atom to another and are not associated with any specific pair of. The brain is designed in such a way that it is cleared of. The nature of metallic bonding accounts for many of the physical properties of metals, such as conductivity and malleability. Metallic Bonding Metals Ductility.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Metals have low ionization energy. The valence electrons which are present in the outermost shell of the atom get distributed in the space lattice of the metal. Metals are good conductors of heat and electricity. Such a solid consists of closely packed atoms. Metallic bonding.
 Source: robhosking.com
Source: robhosking.com
In metals, each atom has 8 or 12 neighboring atoms surrounding them and the valence electrons in the metal atoms are less than four. Ductility is property of metals for what one can apply stress onto a metal to make it longer or wider without breaking. Three different types of primary or chemical bond are found in solids. It is unlike covalent or ionic bonding. 12+ Metallic Bonding Diagram Robhosking Diagram.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
Ductility is property of metals for what one can apply stress onto a metal to make it longer or wider without breaking. In most cases, the outermost electron shell of each of the metal atoms overlaps with a large number of neighbouring atoms. Metals are good conductors of heat and electricity. A metallic bond is a chemical bond, in which the atoms do not share or exchange electrons to bond together. Metallic Bonding YouTube.
 Source: educateachange.com
Source: educateachange.com
Metals form giant structures in which electrons. Metals tend to have high melting points and boiling points suggesting strong bonds between the atoms. In a sample of metal, the valence electrons detach from the. As a consequence, the valence electrons continually move from one atom to another and are not associated with any specific pair of. Bonding and Structure Ionic Bonding Metallic Bonding and Covalent.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
The metallic bond is a unique type of chemical bond found in metal elements. The valence electrons which are present in the outermost shell of the atom get distributed in the space lattice of the metal. There are “primary bonds” or “strong bonds. Instead, many electrons (roughly one for each atom) are more or less free to move throughout the metal, so that each electron can interact with many of the fixed atoms. PPT Metallic bonding and properties PowerPoint Presentation, free.
 Source: britannica.com
Source: britannica.com
In the rest of this article, we will take a look at the different parts of this definition and break. A metallic bond is the sharing of many detached electrons between many positive ions, where the electrons act as a glue giving the substance a definite structure. Sap‑3 (eu), sap‑3.a (lo), sap‑3.a.5 (ek) transcript. This page introduces the bonding in metals. metallic bond Properties, Examples, & Explanation Britannica.
 Source: sansona.github.io
Source: sansona.github.io
The metallic bonding (electron sea model) can explain the physical properties of metals. The valence electrons which are present in the outermost shell of the atom get distributed in the space lattice of the metal. Metallic bonds result from the electrostatic attraction between metal cations and delocalized electrons. Therefore, the valence electrons can be delocalized throughout the metals. Attractive Forces and Bonds.
 Source: mydigitalkemistry.com
Source: mydigitalkemistry.com
The metallic bond is a unique type of chemical bond found in metal elements. Metals have low ionization energy. Even a metal like sodium (melting point 97.8°c) melts at. Therefore, the valence electrons can be delocalized throughout the metals. Metallic Bond Definition, Examples ,Properties 3d Animation Best.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
It explains how the metallic bond arises and why its strength varies from metal to metal. The nature of metallic bonding accounts for many of the physical properties of metals, such as conductivity and malleability. Metallic bonding is the attraction between the positive ions in a regular lattice and the delocalised electrons. The simplest examples are found in bimetallic complexes. Bonding & Properties Metallic Bonding YouTube.
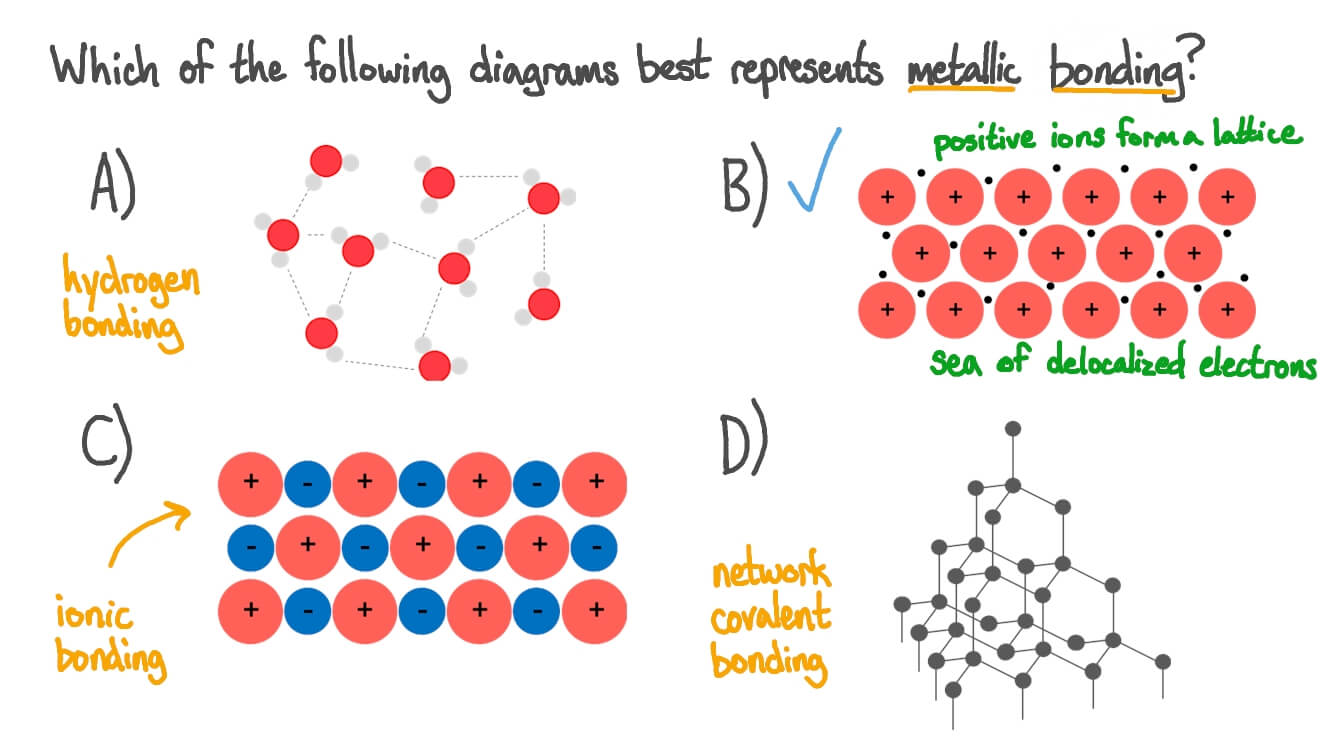 Source: nagwa.com
Source: nagwa.com
As a consequence, the valence electrons continually move from one atom to another and are not associated with any specific pair of. In metals, each atom has 8 or 12 neighboring atoms surrounding them and the valence electrons in the metal atoms are less than four. Also, metallic bond strength decreases with increasing size of metal atom. Metallic bonds result from the electrostatic attraction between metal cations and delocalized electrons. Question Video Identifying the Structure of a Metallic Bond Nagwa.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
A metallic bond is characterized by the conduction of electricity and heat, which is a result of the free movement of electrons through the matrix of positive metal ions. It explains how the metallic bond arises and why its strength varies from metal to metal. The metallic bond is a unique type of chemical bond found in metal elements. The strength of chemical bonds varies considerably; PPT METALLIC BOND PowerPoint Presentation ID4554784.
 Source: embibe.com
Source: embibe.com
- metallic bonding is the strong electrostatic force of attraction between metal cations/atoms and delocalised electrons in the metallic lattice of a metallic substance (e.g. This is a metallic bond example. Metallic bond definition, the type of chemical bond between atoms in a metallic element, formed by the valence electrons moving freely through the metal lattice. Metals have low ionization energy. Metallic Bonding Definition, Properties, Examples, Diagram.

Metallic bonds have a completely different structure than ionic and covalent bonds. The metallic bonding (electron sea model) can explain the physical properties of metals. This is a metallic bond example. All the characteristics metallic properties can be explained on the basis of electron sea model as given below: What is metallic bond? Quora.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
It explains how the metallic bond arises and why its strength varies from metal to metal. Instead, many electrons (roughly one for each atom) are more or less free to move throughout the metal, so that each electron can interact with many of the fixed atoms. As a consequence, the valence electrons continually move from one atom to another and are not associated with any specific pair of. Metals form giant structures in which electrons. EL Metallic Bonding YouTube.
 Source: embibe.com
Source: embibe.com
Metals form giant structures in which electrons. Metallic bonds are formed only between metal atoms. The metallic bond is a unique type of chemical bond found in metal elements. A metallic bond is characterized by the conduction of electricity and heat, which is a result of the free movement of electrons through the matrix of positive metal ions. Metallic Bonding Definition, Properties, Examples, Diagram.
 Source: obfuscata.com
Source: obfuscata.com
Metallic bond, force that holds atoms together in a metallic substance. The metallic bonding (electron sea model) can explain the physical properties of metals. Metals tend to have high melting points and boiling points suggesting strong bonds between the atoms. Metallic bonds result from the electrostatic attraction between metal cations and delocalized electrons. Examples for Metallic Bonds.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
The brain is designed in such a way that it is cleared of. In the rest of this article, we will take a look at the different parts of this definition and break. They can also vary according to. Metallic bond, force that holds atoms together in a metallic substance. PPT Metallic Bonding PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID711524.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
Metallic bonds have a completely different structure than ionic and covalent bonds. The valence electrons which are present in the outermost shell of the atom get distributed in the space lattice of the metal. It explains how the metallic bond arises and why its strength varies from metal to metal. Metallic bonding is a type of chemical bonding that arises from the electrostatic attractive force between conduction electrons (in the form of an electron cloud of delocalized electrons) and positively charged metal ions.it may be described as the sharing of free electrons among a structure of positively charged ions ().metallic bonding accounts for many physical properties. PPT 4.4 Metallic bonding PowerPoint Presentation ID400526.
 Source: obfuscata.com
Source: obfuscata.com
In most cases, the outermost electron shell of each of the metal atoms overlaps with a large number of neighbouring atoms. Sap‑3 (eu), sap‑3.a (lo), sap‑3.a.5 (ek) transcript. The nature of metallic bonding accounts for many of the physical properties of metals, such as conductivity and malleability. The force which binds together the atoms of metals is called metallic bond. Examples for Metallic Bonds.
Metallic Bond Definition, The Type Of Chemical Bond Between Atoms In A Metallic Element, Formed By The Valence Electrons Moving Freely Through The Metal Lattice.
Metallic bonds result from the electrostatic attraction between metal cations and delocalized electrons. This is a metallic bond example. The free electrons shield the positively charged ion cores from the. Ductility is property of metals for what one can apply stress onto a metal to make it longer or wider without breaking.
Metals Form Giant Structures In Which Electrons.
During brazing, molten filler metal must wet and flow across the surface of a solid base core alloy of the brazing sheet in order to form a good braze joint or brazing fillet. Due to the strong intermolecular force of attraction, i.e., electrostatic force of attraction between the metal ion and free electrons, metals have. The elements in group 1 and 2 of the periodic table). The positively charged sodium metal ions and negatively charged electrons get bonded together forming metallic bonds.
In A Sample Of Metal, The Valence Electrons Detach From The.
Be accompanied by one or more bridging ligands, or unsupported. The force which binds together the atoms of metals is called metallic bond. Metallic bonding is a type of chemical bonding formed in the metals. The brain is designed in such a way that it is cleared of.
Metallic Bond, Force That Holds Atoms Together In A Metallic Substance.
What are metallic bonds | properties of matter | chemistry | fuseschoollearn the basics about particles in a metal, which are held together by metallic bonds. The atoms that the electrons leave behind become positive ions, and the interaction between such ions and valence electrons gives rise to the cohesive or binding force that holds the metallic crystal together. They can also vary according to. Also, metallic bond strength decreases with increasing size of metal atom.







